How can renewable energy be used in the built environment?
The ‘built environment’ includes buildings and structures of all kinds, including residential homes and apartments, commercial offices, and facilities in sectors such as retail, education, health, entertainment, defence, and many others.
Buildings account for more than half of Australia’s electricity consumption and are a major driver of ‘peak demand’ or spikes of demand for electricity. On-site renewable energy generation coupled with energy efficiency, smart building controls and energy storage can help reduce the load buildings place on the electricity grid, improve grid management and help reduce energy costs for households and businesses.
Renewable energy and related technologies relevant to the built environment include:
Electricity generation
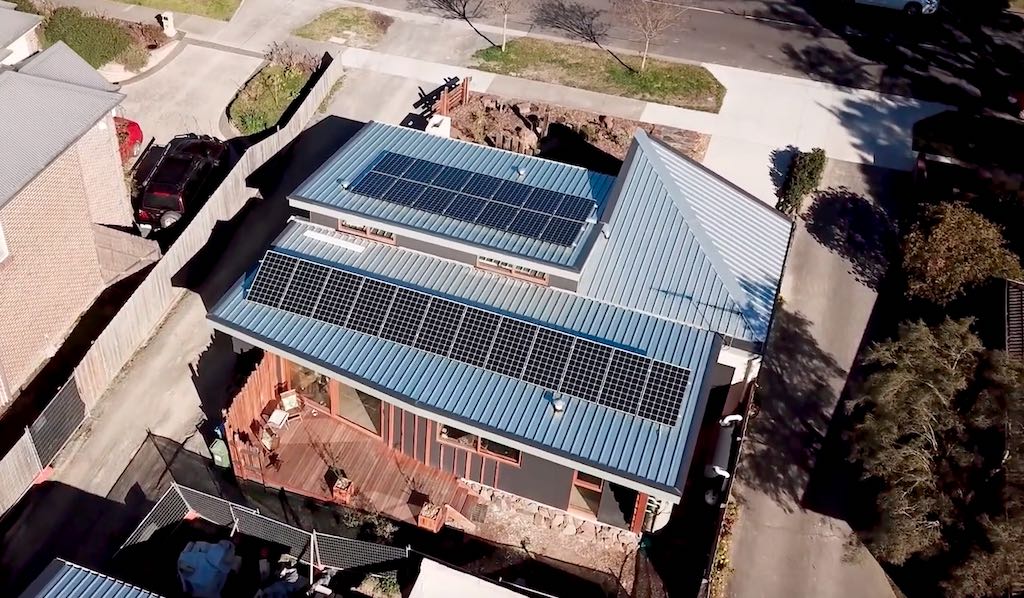
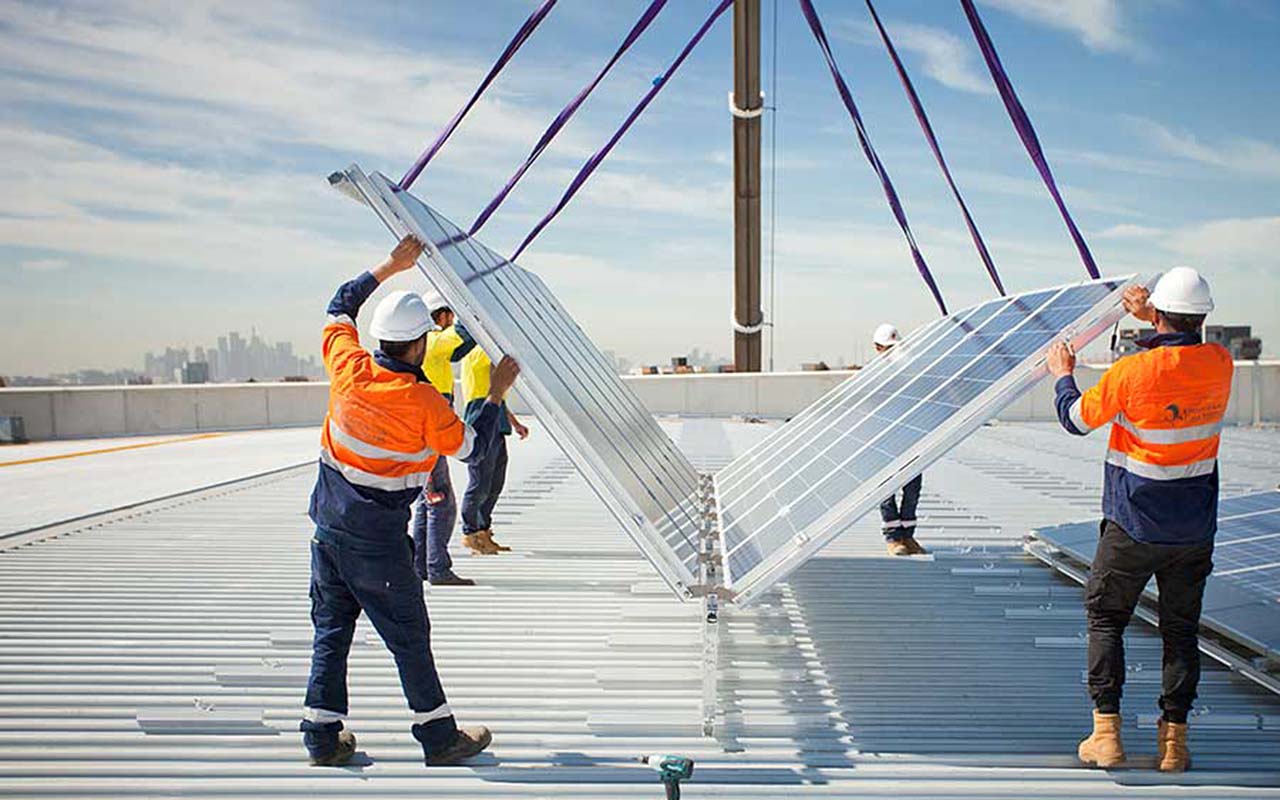
- Rooftop photovoltaic (PV) systems, which generate electricity directly from the sun using solar panels usually mounted on the roof
- Building integrated PV systems, which generate electricity directly from the sun using solar panels that are integrated into building structures, either on the roof, walls or even windows (using transparent panels) in some cases
Hot water systems
- Solar thermal systems, which heat water directly from the sun
- Heat pumps, which heat water using warmth from the surrounding air, water or ground
Solar heating and cooling systems
- Solar thermal cooling, which uses the heat of the sun to drive cooling and/or dehumidification processes
- Solar heating systems such as heat pumps, which draw and boost heat from the surrounding air, water or ground
- ‘Passive’ solar design solutions, which naturally heat or cool buildings without the need for ‘active’ heating and cooling systems
Energy storage systems such as batteries and thermal storage including hot water storage and storage of warmth and “coolth” in building structures
Control systems that manage the flow of energy into and out of properties to increase the total amount of renewable energy used.
Explore renewables in buildings resources
Renewables in Australian buildings
Australia leads the world (on a per person basis) in its rate of rooftop PV installations – around 30 per cent of homes have installed PV. Solar water heaters and air-source heat pumps are used for water heating and space conditioning.
Uptake of other renewable technologies in the Australian built environment has been much more limited. Despite high solar availability and increasing energy prices the uptake of other solar heating and cooling technologies has been quite limited.
Some of the barriers to uptake are: high initial cost; lack of awareness of these technologies and their benefits; lack of suppliers and technicians trained in the technologies; technical and financial risks for businesses using these systems; ‘split incentives’ between building owners or manages and the building occupants.
How are we supporting renewables in buildings projects?
Our purpose is to support the global transition to net zero emissions by accelerating the pace of pre-commercial innovation, to the benefit of Australian consumers, businesses and workers. By connecting investment, knowledge and people to deliver energy innovation, we are helping to build the foundation of a renewable energy ecosystem in Australia.
We have been supporting projects to demonstrate and help commercialise technologies that will increase renewable energy generation and use in the built environment. We have identified that major opportunities in this sector relate to integrating on-site energy generation (i.e rooftop solar) and then using renewable energy to heat and cool buildings and create hot water, which accounts for over half of all energy used in buildings.
These projects are helping building owners and operators to understand the opportunities that arise from integrating renewable energy into their structures. The projects are also assisting energy retailers and network and energy market operators to understand the challenges and opportunities of integrating increasing amounts of renewable energy into buildings.
More information about our renewable energy ‘integration’ projects can be found on the distributed energy resources webpage.
Knowledge sharing
We share knowledge, insights and data from our funded projects to help the renewable energy industry and other projects learn from each other’s experiences.
Read renewables in buildings project reports in the Knowledge Bank