What are batteries?
Batteries are an energy storage technology that uses chemicals to absorb and release energy on demand. Lithium-ion is the most common battery chemistry used to store electricity.
Coupling batteries with renewable energy generation allows that energy to be stored during times of low demand and released (or dispatched) at times of peak demand.
Unlike many other forms of energy storage and generation, batteries are particularly valuable because they provide flexibility. They can respond faster than other energy storage or generation technologies, and help maintain grid stability by turning on and off in fractions of a second.
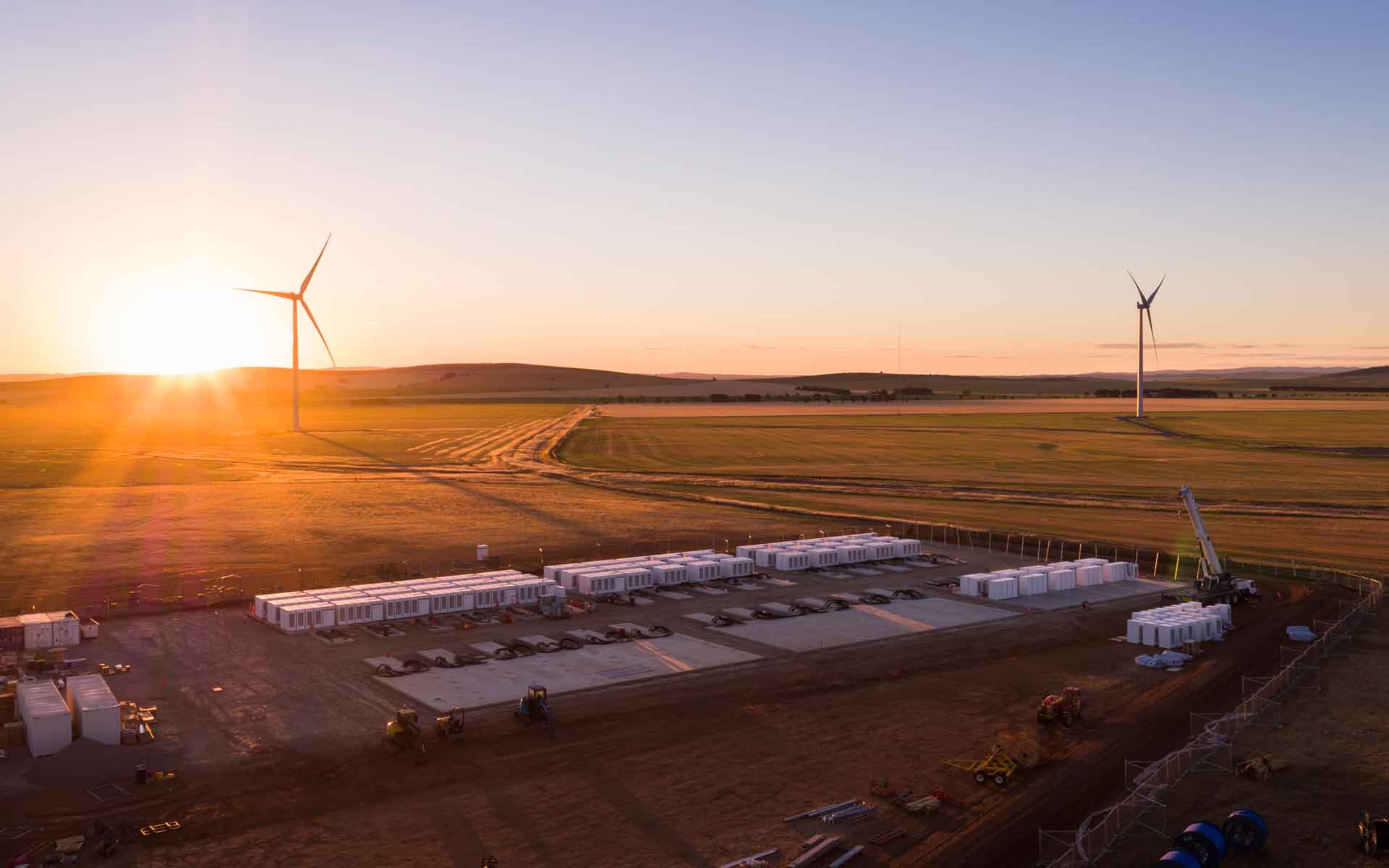
Batteries can be located in a range of areas and installed in small or large quantities for different uses. For example, a large number of batteries installed together, known as grid-scale or large-scale battery storage (LSBS), can act as a large-scale power generator connected into the electricity transmission system.
Smaller-scale batteries can be installed in homes to provide backup power, but can also be operated as a collective in what is called a Virtual Power Plant (VPP).
Due to the technology’s versatility and falling costs, the use of batteries for renewable energy is expected to increase over the coming years.
Explore battery storage resources
Battery storage in Australia
Battery use in the Australian electricity grid is expected to keep growing due to technological advances and rapid cost declines. A number of government schemes have also driven down battery costs and subsidies, accelerating the adoption of the technology by Australian energy producers and users.
In Australia, battery storage for renewable energy is increasingly used in a variety of designs, purposes, sizes and locations. Batteries are used in –
- The national electricity grid (at both the transmission and distribution levels)
- ‘Behind the meter’ in homes, businesses or industrial operations
- The fringes of the grid (areas of poor connection) or off grid (e.g. in microgrids).
How are we supporting battery storage technology?
Our purpose is to support the global transition to net zero emissions by accelerating the pace of pre-commercial innovation, to the benefit of Australian consumers, businesses and workers. By connecting investment, knowledge and people to deliver energy innovation, we are helping to build the foundation of a renewable energy ecosystem in Australia.
We provide funding support for projects involving battery storage because the technology helps the grid to remain stable due to its ability to respond to changes in energy demand. Cost-effective battery storage has the potential to significantly assist in operating a power grid with a higher share of renewable energy.
We deliver impact by supporting a variety of battery projects, from behind the meter, in a range of off-grid and fringe-of-grid applications, and in large-scale applications on the grid. The adoption of these technologies can assist in ensuring that renewable energy continues to contribute effectively in all of Australia’s power systems, therefore allowing a higher penetration of renewables.
Knowledge sharing
We share knowledge, insights and data from our funded projects to help the renewable energy industry and other projects learn from each other’s experiences.
Read battery storage project reports in the Knowledge Bank